What Are Security Automation Tools?
Security automation tools perform routine IT security tasks like breach detection, response, configuration, and compliance to reduce human error, ensure consistency, and free up security teams for more strategic work. Modern security tools leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning to analyze data, identify anomalies, and automate responses in real time, enhancing efficiency and scalability for organizations.
Types of security automation tools include:
- SOC automation tools: These support operations in an organization’s security operations center (SOC), helping integrate multiple systems and centralize alerts.
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems: SIEMs collect, aggregate, and analyze security data from across a network to detect and respond to security incidents.
- SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) platforms: These platforms automate and orchestrate workflows between different security tools to streamline incident response and investigation.
- XDR (Extended Detection and Response) solutions: XDR extends EDR capabilities to cover multiple security data sources, including endpoints, networks, and cloud systems, to provide a comprehensive view for threat detection and response.
- Vulnerability management tools: These tools automate the process of identifying, evaluating, and remediating vulnerabilities in software and systems, often including automated assessment scans.
- Security configuration management tools: These automate and simplify the monitoring and enforcement of configurations for various assets.
The range of security automation tools includes standalone utilities as well as integrated platforms that cover multiple parts of the cybersecurity workflow. Examples include systems that automatically correlate security events, launch investigations, block attacks, and remediate vulnerabilities. Adoption of these tools has accelerated as organizations face a surge in cyber threats and a shortage of skilled security professionals.
Benefits of Security Automation Tools
Security automation tools offer measurable advantages to organizations by enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of security operations. By automating routine processes and improving threat response, these tools help teams manage growing security demands with limited resources.
- Faster threat detection and response: Automation reduces the time between threat identification and response by executing predefined actions instantly, such as isolating affected systems or blocking malicious traffic.
- Reduced manual workload: Repetitive tasks like alert triage, log parsing, and data correlation are handled automatically, freeing security analysts to focus on more complex issues.
- Improved accuracy and consistency: Automated systems follow defined logic and rules, minimizing human error and ensuring that actions are performed consistently across incidents and environments.
- Scalability of security operations: As infrastructure and data volumes grow, automation allows security operations to scale without requiring a proportional increase in staff.
- Enhanced incident investigation: Tools can collect, enrich, and correlate data from multiple sources, providing context and insights that accelerate root cause analysis.
- Continuous compliance monitoring: Automation helps maintain compliance by continuously checking configurations, logging activity, and enforcing policy controls in real time.
- Resource optimization: Organizations can better utilize existing staff and infrastructure by automating lower-value tasks and prioritizing resources for critical threats.
Core Categories of Security Automation Tools
SOC Automation
SOC automation refers to tools and technologies that streamline operations within a security operations center (SOC). These tools integrate disparate systems, centralize alert management, and automate workflows such as escalation, case management, and notification processes. By automating repetitive and low-level SOC tasks, these tools help improve incident response times and free up security analysts to handle more complex, judgment-based work.
Additionally, SOC automation platforms incorporate analytics to prioritize alerts and recommend response actions. Machine learning models and playbooks are commonly used to identify threats, make decisions, and guide investigations. SOC automation increases the efficiency of security teams, reduces manual effort, and enhances the organization’s ability to mitigate threats as soon as they’re identified.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
A SIEM system collects, aggregates, and analyzes log and event data from across an organization’s IT infrastructure. By providing centralized visibility into security-related information, SIEM tools enable the detection of anomalous behavior, policy violations, and cyberattacks in real-time. Automated correlation rules and analytics allow SIEMs to surface patterns or threats that might otherwise go unnoticed.
SIEM tools also play a central role in compliance reporting and forensic investigations. They maintain historical records of events, which can be searched and analyzed long after an incident occurs. Modern SIEM solutions increasingly incorporate automated alerting, threat intelligence integration, and response features, bridging the gap between detection and reaction to simplify incident management.
Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR)
SOAR platforms combine automation, orchestration, and incident response in a unified environment. Their primary function is to coordinate multiple security tools and processes, allowing organizations to develop repeatable, automated response workflows called playbooks. These playbooks execute actions such as gathering threat intelligence, isolating compromised endpoints, and deploying countermeasures without manual intervention.
A key benefit of SOAR tools lies in their ability to integrate with a broad array of security products—from endpoint security to threat intelligence feeds—and unify data streams for more effective correlation and decision-making. SOAR solutions often include case management and collaboration features, helping security teams manage incidents from detection to resolution within a single interface. This results in faster, more consistent incident handling and improved operational visibility.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
XDR platforms provide comprehensive threat detection and response by integrating data across endpoints, networks, cloud services, and other security layers. Unlike traditional security solutions, XDR offers unified visibility and response automation, correlating events from multiple sources to identify advanced threats that span different parts of the IT environment.
By automating the aggregation, analysis, and response to incidents, XDR reduces the noise from disparate tools and helps security teams take coordinated action quickly. Features such as automated investigation, guided remediation, and continuous monitoring provide enhanced protection against both known and unknown threats, enabling organizations to respond with greater speed and confidence.
Vulnerability Management Automation
Vulnerability management automation tools continuously scan IT assets—infrastructure, applications, and cloud environments—for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. These tools prioritize findings based on risk, automate remediation workflows, and generate actionable reports for IT and security teams. Automation ensures vulnerabilities are discovered and addressed quickly, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers.
These solutions can integrate with patch management or configuration systems to fully automate the cycle from detection to remediation and verification. By minimizing manual steps and ensuring up-to-date coverage, vulnerability management automation strengthens organizational security and eases the burden of regulatory compliance.
Security Configuration Management Tools
Security configuration management tools automate the enforcement and monitoring of secure configurations for assets like servers, workstations, network devices, and cloud resources. They help ensure systems are configured according to internal policies or industry standards, such as CIS Benchmarks or PCI DSS, reducing the risk of misconfiguration—a leading cause of data breaches.
These tools provide continuous compliance monitoring, reporting, and automated remediation for configuration drift. They often integrate with CI/CD pipelines and cloud management platforms, allowing organizations to maintain secure baselines as their environments evolve. This automation not only reduces configuration errors but also supports audit readiness and regulatory requirements.
Notable Security Automation Tools
SOC Automation Tools
1. Radiant Security
Radiant Security is an Agentic AI SOC platform that automates alert triage, investigation, and response across the security lifecycle. The platform is designed to reduce false positives by roughly 90%, enabling analysts to spend more time on verified threats rather than manual triage. Radiant also aims to shorten investigation and response times (MTTR) and lower operational costs, while helping teams avoid the fatigue that often comes with high alert volume.
Key capabilities include:
- Agentic AI triage and investigation for all alert types, including previously unseen or low-fidelity ones.
- Transparent reasoning that shows how and why the AI reached its conclusions, helping analysts validate decisions and build trust.
- Integrated response with one-click, executable action plans that can be carried out manually or automated when appropriate.
- Log management with unlimited retention, delivered at a cost significantly lower than traditional SIEM platforms.
- AI feedback loop that allows teams to influence and adjust triage behavior using environmental context, improving accuracy over time.
Radiant provides a unified environment for handling alerts, investigations, response actions, and log data, with an emphasis on efficiency, clarity, and analyst control.
2. Swimlane
Swimlane is a low-code security automation platform that centralizes and accelerates security operations. It allows teams to build and automate workflows without writing code, making it easier to handle alert triage, case management, and threat response. Swimlane integrates with a range of tools, enabling dynamic data collection, enrichment, and action across the SOC.
Key features:
- Low-code visual workflow builder for custom automation
- Integration with hundreds of security and IT tools
- Automated alert triage, enrichment, and response
- Real-time reporting and dashboards for SOC performance
- Scalable to support large, complex security environments
3. Vanta
Vanta automates security monitoring and compliance management by continuously checking systems against frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA. While not a traditional SOC automation tool, it aids in automating audit readiness and reducing manual compliance tasks. Vanta connects to cloud platforms, identity providers, and other services to verify controls, generate evidence, and track remediation.
Key features:
- Automated compliance checks for multiple frameworks (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001)
- Integrates with cloud infrastructure and third-party services
- Real-time monitoring of control status and risks
- Evidence collection and audit readiness automation
- Alerts and task tracking for remediation and policy enforcement
Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR) Tools
4. Splunk SOAR
Splunk SOAR enables security teams to automate their entire incident response lifecycle—from threat detection to containment. Using playbooks, teams can create repeatable response actions triggered by specific events. It integrates with security tools and uses visual editors to simplify automation development. Splunk SOAR also includes case management, threat intelligence ingestion, and data enrichment capabilities.
Key features:
- Playbook-based automation of incident response
- Visual editor for designing and managing workflows
- Integration with hundreds of third-party security tools
- Case management and collaboration features
- Threat intelligence enrichment and automated decision-making
5. IBM Security QRadar SOAR
QRadar SOAR helps coordinate incident response by automating tasks, managing cases, and providing guided workflows. It connects with IBM’s broader security ecosystem and third-party tools to orchestrate response actions across the environment. The platform includes dynamic playbooks, collaboration, and post-incident analysis. It also supports regulatory requirements through audit trails and reporting.
Key features:
- Dynamic playbooks for automated response
- Integration with IBM QRadar and other security tools
- Case management with evidence tracking and audit trails
- Built-in collaboration and task assignment features
- Post-incident review and reporting for continuous improvement
6. Microsoft Sentinel
Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud-native SIEM and SOAR platform that provides security analytics and automated response across Azure and hybrid environments. It leverages AI to detect threats and offers automation capabilities through playbooks powered by Azure Logic Apps. Sentinel can orchestrate responses like account suspension or IP blocking across Microsoft and non-Microsoft systems.
Key features:
- Cloud-native integration with Azure services and hybrid environments
- AI-driven detection and analytics for faster threat identification
- Automated response via playbooks using Azure Logic Apps
- Integration with Microsoft Defender and third-party tools
- Built-in threat intelligence and investigation tools
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools
7. Exabeam
Exabeam is a SIEM platform that uses behavior analytics and machine learning to improve threat detection and reduce alert fatigue. Instead of relying only on predefined rules, Exabeam builds baselines of normal user and entity behavior, then flags deviations that could indicate compromise. Its Smart Timelines feature automatically stitches together related events across systems, simplifying investigations and accelerating response.
Key features:
- User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) for advanced threat detection
- Automated incident timelines with Smart Timelines
- Integration with a wide range of security and IT tools
- Machine learning models to reduce false positives
- Support for compliance reporting and forensic investigations
8. Splunk Enterprise Security
Splunk Enterprise Security is a scalable SIEM solution that provides real-time visibility into machine data from across the enterprise. It applies correlation searches, risk-based alerting, and adaptive response actions to detect and respond to threats. Splunk ES includes data visualization, analytics, and integration options.
Key features:
- Real-time monitoring and alerting across large data sets
- Risk-based alerting to prioritize threats
- Integration with over 1,000 third-party tools via Splunkbase
- Visual analytics and dashboards for security posture insights
- Supports compliance and incident investigation workflows
9. ArcSight
ArcSight is a SIEM platform from OpenText that collects and analyzes security data for threat detection and compliance. It features correlation and anomaly detection engines to identify suspicious activity and supports both on-prem and cloud deployments. ArcSight’s open architecture allows integration with threat intelligence feeds, third-party tools, and automation platforms.
Key features:
- Scalable log collection and centralized analysis
- Real-time correlation and anomaly detection
- Integration with threat intelligence sources and automation tools
- Support for hybrid and multi-cloud environments
- Built-in compliance reporting and auditing capabilities

Extended Detection and Response (XDR) Tools
10. Microsoft 365 Defender
Microsoft 365 Defender is an XDR solution that unifies threat protection across Microsoft 365 services, including email, endpoints, identity, and cloud apps. It correlates signals across these domains to detect and respond to coordinated attacks, using automation to investigate incidents and initiate remediation. Defender integrates with Microsoft Sentinel and other tools in the Microsoft security stack.
Key features:
- Cross-domain threat correlation (email, identity, endpoints, cloud)
- Automated investigation and remediation of alerts
- Deep integration with Microsoft 365 and Azure services
- Built-in threat intelligence from Microsoft’s global sensor network
- Unified incident management across Microsoft products
11. Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR
Cortex XDR extends detection and response capabilities by combining data from endpoints, networks, and cloud environments. It uses machine learning to detect known and unknown threats, while automated root cause analysis helps security teams understand attack paths. The platform also supports threat hunting and incident response with telemetry and forensics capabilities.
Key features:
- Unified data from endpoints, networks, and cloud
- Behavioral analytics and ML-based threat detection
- Automated root cause analysis and response
- Advanced threat hunting and investigation tools
- Integration with Palo Alto Networks and third-party products
12. Trend Micro XDR
Trend Micro XDR connects telemetry across email, endpoint, server, and cloud workloads to detect and respond to threats with better context. It includes automated correlation, prioritized alerting, and guided investigation tools that reduce response time. Trend Micro XDR also provides visibility into the full attack lifecycle.
Key features:
- Cross-layer data correlation from multiple security vectors
- Prioritized alerts with contextual threat intelligence
- Guided investigation workflows and playbooks
- Integration with Trend Micro and third-party security tools
- Continuous monitoring for proactive threat response
Vulnerability Management Automation Tools
13. Tenable
Tenable provides automated vulnerability management through continuous scanning of assets across on-premises, cloud, and containerized environments. It prioritizes vulnerabilities based on severity and business risk, offering actionable insights for remediation. With integrations into patch management and security platforms, Tenable helps security teams simplify vulnerability lifecycle management and maintain compliance with industry standards.
Key features:
- Continuous scanning across IT, cloud, and container assets
- Risk-based vulnerability prioritization
- Integration with patch and security tools for remediation
- Comprehensive dashboards and compliance reporting
- Asset discovery and inventory management
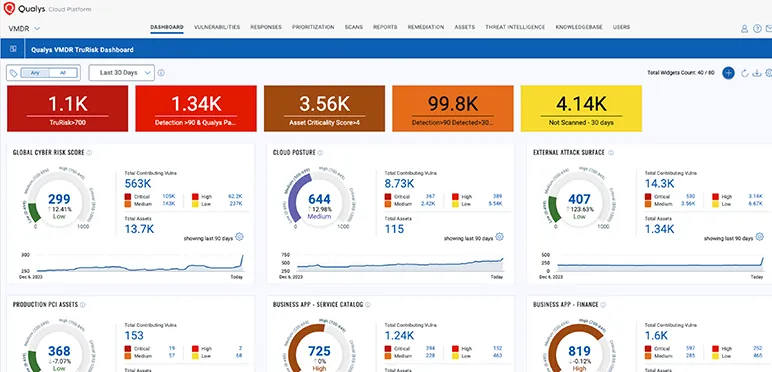
14. Qualys VMDR
Qualys VMDR (Vulnerability Management, Detection, and Response) automates the entire vulnerability management process, from detection to remediation. It provides asset inventory, continuous vulnerability assessment, and patch deployment. By combining vulnerability scanning with threat intelligence and automated workflows, Qualys VMDR reduces exposure time and ensures efficient remediation of critical issues.
Key features:
- Real-time asset discovery and inventory
- Continuous vulnerability scanning and risk scoring
- Integrated patch management and remediation workflows
- Threat intelligence for prioritizing critical vulnerabilities
- Compliance reporting and policy enforcement
15. Rapid7 InsightVM
Rapid7 InsightVM focuses on live vulnerability management, offering dynamic visibility into assets and exposures across hybrid environments. It uses risk-based prioritization to highlight the most impactful vulnerabilities and integrates with ticketing and patching systems for automated remediation. InsightVM also supports dashboards and reporting for technical and executive audiences.
Key features:
- Continuous asset discovery and vulnerability scanning
- Risk-based vulnerability prioritization with threat context
- Integration with ITSM and patching systems
- Real-time dashboards and customizable reporting
- Automated remediation tracking and verification

Security Configuration Management Tools
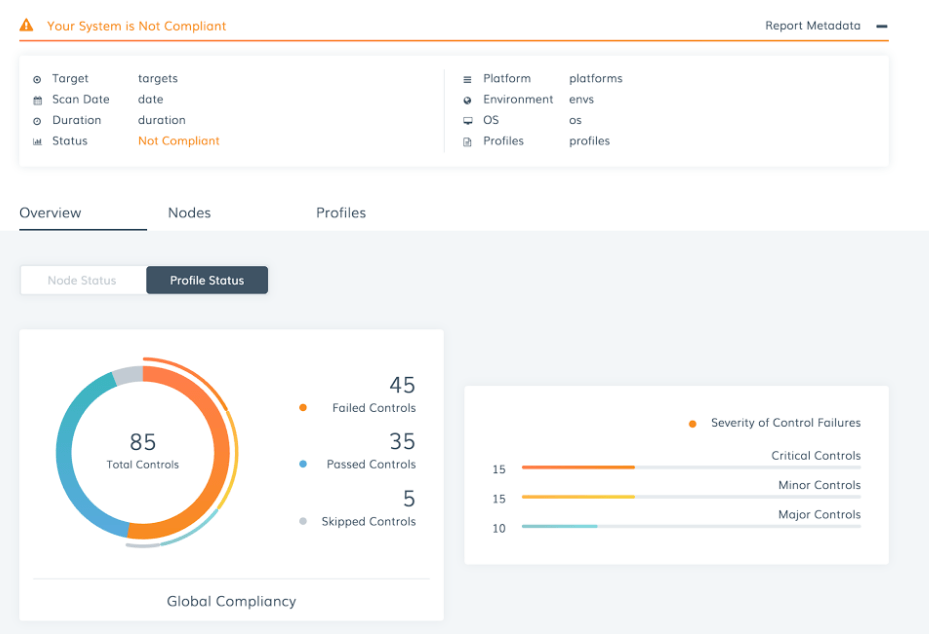
16. Chef InSpec
Chef InSpec is an open-source framework for automating security and compliance checks as code. It allows teams to define compliance policies in human-readable language and apply them consistently across servers, containers, and cloud environments. InSpec integrates with CI/CD pipelines to enforce security baselines during development and operations.
Key features:
- Compliance-as-code for consistent enforcement
- Human-readable policy definitions and tests
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines and DevOps workflows
- Automated detection of configuration drift
- Support for multiple frameworks and industry benchmarks
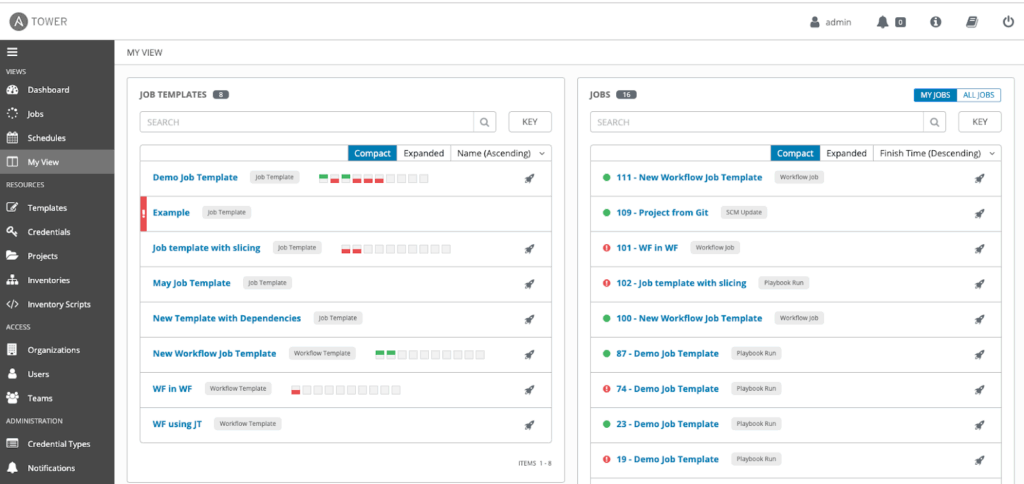
17. Ansible
Ansible provides automated configuration management with modules that enforce secure configurations across infrastructure. Using playbooks, administrators can define and apply security baselines at scale, ensuring consistency across servers, cloud instances, and network devices. Ansible integrates into DevOps pipelines and supports agentless operation.
Key features:
- Declarative playbooks for configuration automation
- Enforcement of security baselines across hybrid environments
- Agentless architecture for simplified deployment
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines and DevOps workflows
- Automated remediation of configuration drift
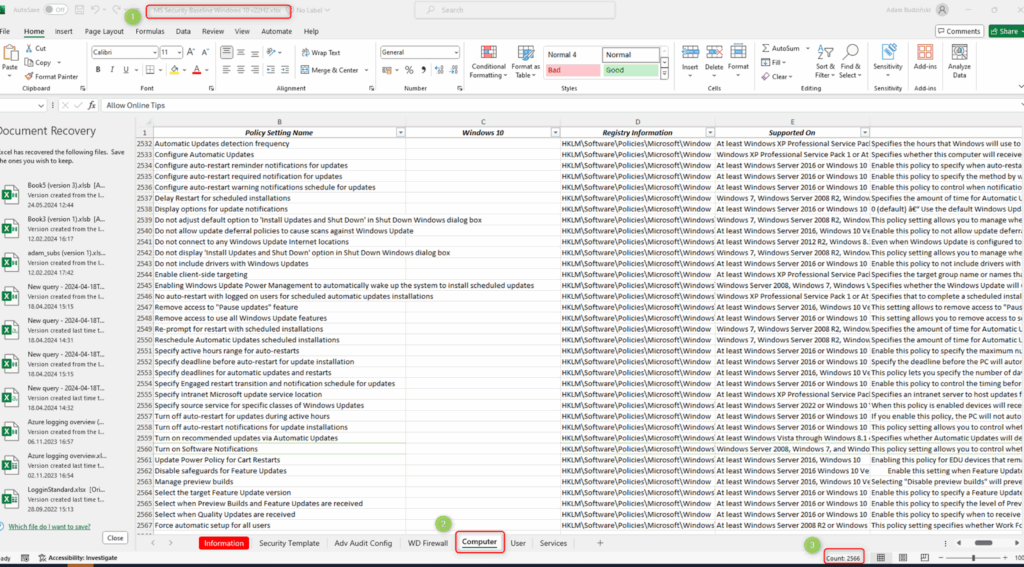
18. Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit
The Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit offers predefined configuration baselines and tools to help organizations secure Windows systems. It provides Group Policy Objects (GPOs), scripts, and templates aligned with Microsoft’s recommended security standards. The toolkit automates the deployment and monitoring of security configurations, supporting audit readiness and compliance across enterprise Windows environments.
Key features:
- Predefined security baselines for Windows systems
- Group Policy Objects (GPOs) for automated configuration
- Scripts and templates for deployment and monitoring
- Alignment with Microsoft security and compliance standards
- Support for audit readiness and regulatory requirement
Conclusion
Security automation is no longer optional for organizations facing an expanding threat landscape and limited security resources. By automating detection, response, compliance, and configuration tasks, these tools reduce operational overhead, improve consistency, and accelerate incident handling. However, to be effective, automation must be implemented thoughtfully, aligned with business objectives, integrated across the environment, and continuously refined to address evolving risks.

